- cross-posted to:
- worldnews@lemmy.ml
- cross-posted to:
- worldnews@lemmy.ml
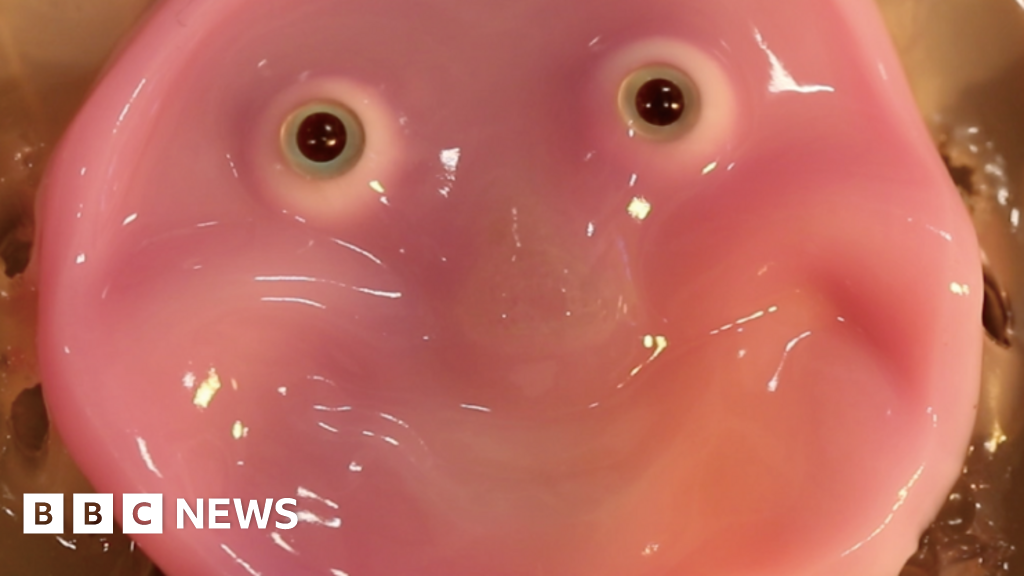
Japanese scientists have found a way to attach living skin to robot faces, for more realistic smiles and other facial expressions.
The breakthrough came from copying tissue structures in people, according to the team at Tokyo University.
The prototype may appear more Haribo than human-like.
But the researchers say it paves the way to making convincingly realistic, moving humanoids with self-healing skin that will not easily rip or tear.


This is the best summary I could come up with:
Japanese scientists have found a way to attach living skin to robot faces, for more realistic smiles and other facial expressions.
The prototype may appear more Haribo than human-like.But the researchers say it paves the way to making convincingly realistic, moving humanoids with self-healing skin that will not easily rip or tear.
In people, the skin is tethered to underlying structures by ligaments - tiny ropes of flexible collagen and elastane.
To recreate that, the researchers drilled lots of little holes into the robot and applied a gel containing collagen, and then the layer of artificial skin on top.
“Another important challenge is creating human-like expressions by integrating sophisticated actuators, or muscles, inside the robot,” Prof Takeuchi said.
But the work may also be useful in research into skin ageing, cosmetics and surgical procedures, including plastic surgery.
The original article contains 307 words, the summary contains 137 words. Saved 55%. I’m a bot and I’m open source!